Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition in people with the diabetes where chemicals called “ketones” accumulate in the blood which can be toxic to the body. This is a warning sign that a blood sugar is not controlled well.
How does DKA happen?
The body normally breaks down sugar for energy. But when the body is unable to break down the sugar due to lack of insulin, your body starts burning the fat cells which produce ketones. Both type I and type II diabetics are at risk for DKA.
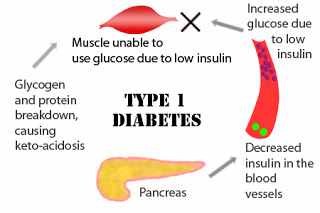
What are the reasons for DKA?
- Lack of insulin. This can occur if you are not taking adequate insulin dosage, if you missed a dose of insulin or if you did not realize that he have diabetes and hence not on any treatment.
- Due to illness such as an infection or lack of food intake.
- Insulin pump not working properly.
- Taking certain medications or substance abuse.
Symptoms of DKA
- Increased thirst or dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- Abdominal pain
- High blood sugar levels
- Ketones in the urine
- Sweet or fruity smell in the breath
- Feeling excessively tired
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hard to concentrate or confusion
- How is DKA diagnosed
- DKA is diagnosed with blood and urine tests.
What do I do if I think I have DKA?
You can test for ketones at home with urine test strips at home. Call your doctor or nurse immediately if you have any of the above symptoms or if your blood sugars are consistently high (generally above 240mg/dL).
How is DKA treated?
Intravenous insulin should be given immediately. When you have DKA, you will have a deficiency of electrolytes including sodium and potassium that need to be replaced adequately, to prevent other serious complications
How to prevent DKA?
- Strict blood sugar control.
- Taking adequate insulin.
- When he have an illness such as an infection, if he her oral intake is not adequate, if he had surgery, your blood sugars need to be checked frequently during this illness to make sure that your blood sugars are not going up to high are too low.
- Do not exercise if your blood sugar is very high or if your urine has ketones.
