Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
The diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mainly depends on the level of blood sugar in the blood. There are currently 4 ways to diagnose diabetes.
- Fasting Blood Sugar: This is the most common test that is used for diagnosing diabetes as it is a simple and convenient test. In this test, blood sugar is taken after a fast of 8 hours. Fasting means that you should not eat or drink (except water) for 8 hours. This is usually done in the morning before eating breakfast. A normal fasting blood sugar is a level less than 100 mg/dL. A fasting blood sugar of 126 mg/dL or more, satisfies a diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Oral glucose tolerance test:This test checks the body’s capacity to lower the blood sugar after taking a concentrated amount of glucose. This also needs fasting for 8 hours prior to the test. After fasting blood sugar is taken, 75 grams of glucose dissolved in water is ingested. Blood is drawn again after the 1st and 2nd hour. If the blood sugar on the 2nd hour is more than or equal to 200mg/dl, diabetes is considered.
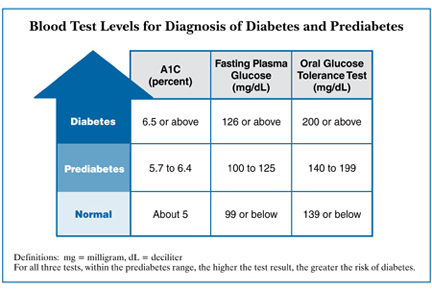
- Glycosylated Hemoglobin (Hemoglobin A1C or Hgb A1C) Level: This determines the level of control of blood sugar in the last 2 to 3 months. It checks the level of sugar that has attached to the red blood cell. A level of 6.5% or greater is diagnostic of diabetes.
- Random Blood Sugar of at least 200 mg/dl with signs and symptoms of diabetes: This test has the lowest reliability and should be confirmed with another test in diagnosing diabetes.

Pingback: Melissa Tower (melissatower) | Pearltrees