There are an extensive range of medications available to treat both Type 2 diabetes. These medications come in a range of forms, from injectable medications to oral tablets. This article will provide a brief overview of the various oral medications that are available, how they work and their side effects.
Metformin (Glucophage)
How it works:
Metformin is the mainstay treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes especially if there is associated obesity. It decreases the synthesis and release of sugars by the liver. Moreover, it increases the sensitivity of body tissues to the secreted insulin (decreases insulin resistance).
Caution with:
- People with heart, liver or kidney problems
Side Effects:
- Muscle aches
- Numbness in the extremities
- Stomach pain
- Dizziness
____________________________________________________________
Sulfanylureas (Glipizide/ Glyburide/ Glimepiride)
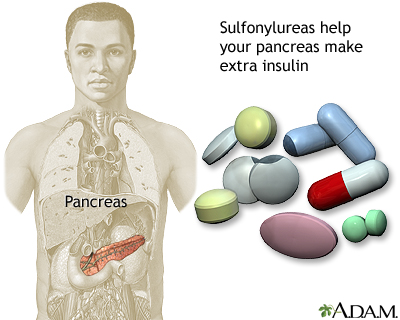 How it works:
How it works:
Encourages pancreas (insulin secreting structure of body) to secrete a higher level of insulin (glucose lowering hormone) and therefore reduces the level of blood sugar
Caution with:
- People with heart, liver or kidney problems
Side Effects:
- Increase in Weight
- Irritated Skin and Rashes
- Low Levels of Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Acarbose
How it works:
Reduces blood sugar levels by reducing the digestion of starch in the gut and by hampering the release of digested glucose into the bloodstream
Caution with:
- People with bowel or digestion issues
Side Effects:
- Stomach Cramps
- Diarrhea
- Excess Gas (Flatulence)
- Reduces appetite
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Rosiglitazone (Avandia)/ Pioglitazone (Actos)
How it works:
Improves the sensitivity of body tissues to secreted insulin (reduces insulin resistance)
Caution with:
- People with heart disease, kidney and liver problems
- People who are malnourished
Side Effects:
- Increased risk of heart failure
- Liver damage
- Body edema (swelling)
- Increased chances of bone fracture in females
- Impaired function of liver enzymes
____________________________________________________________
Sitagliptin (Januvia)
How it works:
It has dual action. It promotes the release of insulin by the pancreas and improves the sensitivity of body tissues to secreted insulin
Caution with:
- People with kidney problems
- Pregnant females
- People with body edema
Side Effects:
- Headache
- Upper respiratory tract infections (flu and cold like symptoms)