Step 1: Learn about Diabetes
Diabetes Basics
The different types of diabetes
♦ Type 1 diabetes – Your body does not produce insulin. Insulin is essential to convert sugar into energy that the body needs for daily living. When you have type 1 diabetes you need insulin daily to live.
♦ Type 2 diabetes – The most common type of diabetes. With type 2 diabetes the body does not produce or use insulin effectively, which is also known as insulin resistance.
♦ Gestational diabetes – This form of diabetes is common in pregnant women in their second trimester. It usually goes away after giving birth. However, there is a chance that these women and their children are at risk of getting diabetes at a later stage.
Remember that your health should be your main concern and you are the most important part of your heath care team.
Learn the best way to manage your diabetes, by consulting your doctor about the best way to cope with your diabetes to keep in good health. Others who are able to help are:
|
 |
Tips on how you can find out more about diabetes
- Learn how to live with diabetes. There are classes that teach you how you can care for yourself when you have diabetes. Ask at your local hospital, health clinic or doctor about these classes.
- Join a support group — personally or online — in an effort to get support from others that are also suffering from diabetes. Check out www.fightdiabetes.com/forum
- Learn about diabetes online.
- Take diabetes seriously. Oftentimes you will hear people refer to their diabetes as their “sugar being a little high” or “touch of diabetes” which implies that diabetes isn’t a serious condition. That is not true. Diabetes is serious; however, there are several ways that you can manage it.
People who have diabetes should have a balanced diet, have a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and take their medication, even when they feel good. Managing your diabetes requires a lot of work, but in the end it is worth it!
Why manage your diabetes?
Caring for yourself and your diabetes will let you feel much better today and later on in life. If your glucose levels are close to normal, you might:
|
 |
Eye problems which could result in difficulty seeing or going blind
Kidney failure
Numbness, tingling or pain in your feet and hands, generally known as nerve damage
Gum and teeth problems
Steps you can take
- Know what type of diabetes you have
- Join support groups
- Learn how taking care of your diabetes makes it possible to feel good today and in the future.
Step 2: Learn your diabetes ABCs
Consult your doctor on how to take care of your A1C, Blood pressure, and Cholesterol (ABCs). This helps to reduce the risk of having a stroke, heart attack or other diabetic complications.
The A1C test (A-one-C)
What is it?This is a blood test that determines your average glucose levels over the last three months. It different from your regular daily blood sugar checks. The importance of the A1C testYou should know your glucose levels over time. It is best to monitor your blood sugar levels to ensure that it does not get too high. If your blood sugar levels are high is can damage your eyes, kidneys, blood vessels, feet and heart. |
 |
What is the goal of the A1C?
For many diabetic people, the A1C goal is under 7. However, it varies from person to person, thus it is important that you learn what your goal needs to be.
B for Blood pressure
What is it?Blood pressure is a way of measuring the force of blood against the walls of the blood vessels when your heart pumps. The importance of blood pressureHigh blood pressure causes your heart to work too hard. It may lead to a stroke, heart attack, and harm your eyes and kidneys. |
 |
What is the blood pressure goal?
For almost all people having diabetes, the blood pressure goal would be under 140/90. It could differ for you. Learn what should be your goal.
C for Cholesterol
What is it?
The two main types of cholesterol in your blood are: HDL and LDL.
HDL or “good” cholesterol helps to eliminate the “bad” cholesterol from your blood vessels.
LDL or “bad” cholesterol can accumulate and block your blood vessels. It may result in a stroke or heart attack.
What would be the HDL and LDL goals?Learn what your cholesterol goals should be. It could differ from others. For those that are over the age of 40, you might have to take a statin drug for cardiovascular health. Steps you can takeConsult with your health care team about:
|
 |
Step 3: Learn how to cope with diabetes
Living with diabetes may involve many emotions- anger, sadness and a sense of feeling overwhelmed. While you may know what steps to take to keep in good health, there may be times when you find it difficult to follow your plan.
|
This section provides you with tips in order to manage your diabetes
|
 |
Healthy food choices
- Ask your health care team to help you create a diabetes meal plan.
- Drink plenty of water and avoid soda and juice.
- Fruits and vegetables, bread, whole grains, cereals, cheese, and skim or low-fat milk are all good choice to eat.
- Eat foods that contain less sugar and salt, trans fat, saturated fat and are lower in calories.
- Include more fiber in your diabetes meal plan by eating crackers, pasta, rice, whole grain cereals and breads.
- Your meal should consist of half a plate of fruit and veggies, 1 / 4 lean protein, like skinless turkey, chicken or beans, and 1 / 4 of whole grain, like whole wheat pasta or brown rice.

Be active
- Set realistic, achievable goals to be more active. Start out slow by walking for 10 minutes, 3 times daily.
- If you are not already at a healthy weight, make it your goal to reach that level through eating well and increasing physical activity.
- Do strength exercise twice a week. This can include anything from push-ups, yoga to even heavy gardening. Learn more
Daily Routine
- Medicine should be taken each day, even on days when you feel good. Consult your doctor about whether you should take aspirin to prevent stroke or heart attack. Inform your doctor if you are unable to pay for your medications or if you experience any adverse reactions.
- Check your blood sugar. You might want to check it several times daily. Make use of the card at the back of this booklet to track your progress. Make sure you discuss it with your health care team.
- Dental care is important for healthy gums and teeth. Brush your teeth twice daily and floss every day.
- Lower high blood pressure and monitor it.
- Make sure that you check your feet daily for cuts, swelling, red spots, and blisters. Get in touch with your health care provider immediately about any blisters that do not disappear.
- Quit smoking. Get help to quit. Call 1-800-QUITNOW (1-800-784-8669).
Consult your health care team
- If you have any questions or concerns about your diabetes, consult your doctor.
- If you notice any changes in your health, inform your doctor immediately.
Steps to take
- Stick to a healthy meal plan.
- Increase physical activity.
- Learn how and when to check your blood sugar and how you can use the results to take care of your diabetes.
- Make use of these tips to take care of yourself.
- Every time you visit your health care team, discuss how your diabetes plan is helping you.
Step 4: Get routine care to stay healthy
You should see your healthcare team at least two times per year to diagnose early signs of problems and treat it.
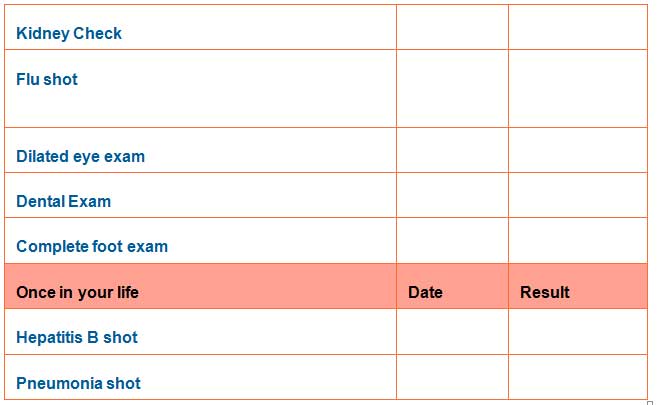
Get at least once in your life a:
- Pneumonia shot
- Hepatitis B shot
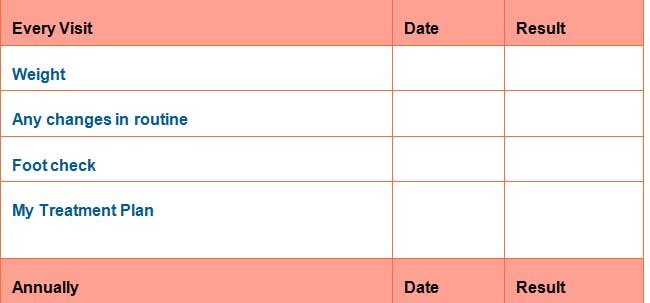
Once a year, remember to have a:
- Urine and a blood test to look for kidney problems
- Flu shot
- Dilated eye exam to look for eye problems
- Dental exam to examine gums and teeth
- Complete foot exam
- Cholesterol test
Twice a year, have an:
- A1C test. It should be checked more regularly if it’s above 7.
At every visit, make sure you have a:
- Blood pressure check
- Foot check
- Weight check
- Review of your self-care plan
Medical health insurance and diabetes
In case you have Medical health insurance, find out if your Medicare covers diabetes care. Medical health insurance covers several of the expenses for:
- Appointments with a dietitian
- Diabetes medication
- Diabetes education
- Diabetes supplies
- Special shoes, if needed
Steps to take
- The card at the back of this booklet can be used to keep track of your diabetes care.
- If you have Medicare health insurance, look at your plan
- Write out your following appointment, both the date and time.
- Ask your health care team if there is any other test that you should take. Learn what the results mean.
Keep in mind that: - You are responsible for your health
- Seek help from your health care team
- Discover ways to achieve your diabetes ABC goals.
- Use the steps in the booklet in order to better manage your diabetes.
My Diabetes Care Record
It is advisable that you keep an organized record of your health information. It will be a useful guide for all your personal diabetes care. The table below includes sections so that you can record your important dates, exams and results. Make sure that you present this card at every visit to your doctor to ensure that you and your health care team understand specifically what’s working for you.
Your diabetes care record provides information on the following:
- The test name or check-up
- When to have the check-up or test
- What your ABC goal should be
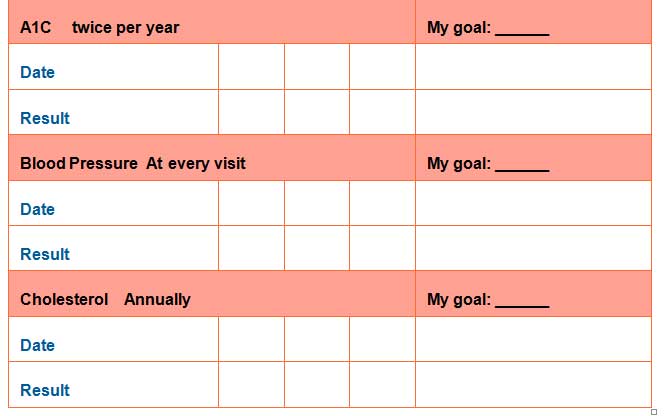
My Diabetes Care Record
How to use the record
This page can be used to record the date and results of every single exam, test or shot.
Self-monitoring for Blood Glucose Levels
Using your card
There are three sections of this card. Each section will be a guide to when to look at your blood glucose: before mealtimes, 1 – 2 hours after mealtimes, and at night. When checking your blood glucose levels you can record the information on your card. Present this card at every visit to your doctor. Discuss your goals as well as your progress in health.
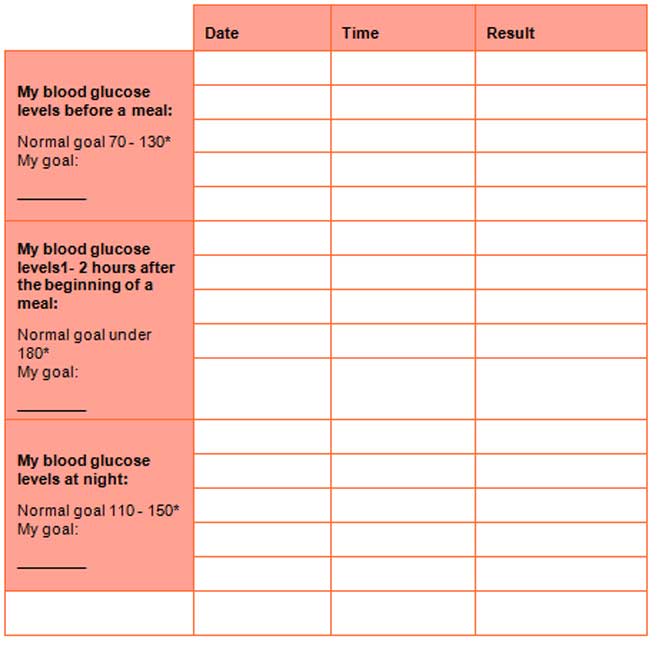
* If you have had diabetes for quite a while or if you are over the age of 65, then your blood glucose targets could be different. It could also vary if you suffer from other health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, or if your blood glucose levels are often too low.
REFERENCE:
http://ndep.nih.gov/publications/publicationdetail.aspx?pubid
